Mental Health Service Use by Persons of Asian Ancestry With DSM-IV Mental Disorders in the United States
Abstract
Objectives:
This study compared the prevalence and odds of mental health service utilization among people of Asian ancestry with lifetime DSM-IV mood, anxiety, alcohol, and drug use disorders with utilization by members of other racial and ethnic groups with similar disorders.
Methods:
Between 2001 and 2002, a total of 43,093 noninstitutionalized individuals were assessed by the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC) study of lifetime prevalence of DSM-IV psychiatric disorders and mental health service utilization among various ethnic and racial groups.
Results:
Among individuals with lifetime mood disorders, Asians had significantly lower mental health service utilization compared with whites (odds ratio [OR]=.31, 95% confidence interval [CI]=.21–.46), Hispanics (OR=.49, CI=.33–71), and Native Americans (OR=.27, CI=.15–.48) but similar utilization compared with blacks. There were no statistically significant differences in lifetime mental health service utilization for alcohol and drug use disorders among racial and ethnic groups.
Conclusions:
Asians with lifetime mood disorders underutilized mental health services even after adjustment was made for socioeconomic variables and years of residency in the United States. Future studies of culture-specific attitudes, correlates, and barriers to mental health service utilization are warranted. (Psychiatric Services 62:1180–1186, 2011)
People of Asian descent are one of the fastest-growing racial and ethnic groups in the United States. In 2008, they represented 4.4% of the total U.S. population, but their numbers are expected to grow by 213% by 2025, rising from 10.7 million to 33.4 million (1). Despite the rapid increase in population and need for provision of mental health services, there is a dearth of empirical research about mental health service utilization patterns among Asians and how they compare with those of other racial and ethnic groups (2,3).
Persons from racial and ethnic minority groups are less likely to utilize mental health services compared with whites (4). Previous studies reported that Asians have a low rate of mental health service use compared with the general population (5–7). Recent nationally representative studies that used DSM-IV diagnostic criteria reported lower prevalence of mental disorders among Asians compared with members of other racial and ethnic groups (2,8–11). Therefore, some researchers have suggested that low prevalence of mental health service utilization among Asians may be due to lower prevalence of mental disorders among Asians (12). Other researchers, on the basis of a conventional belief that Asians are a “model minority,” speculated that greater mental and emotional resiliency among Asians may lead to less need for mental health services (13).
However, the supposition that low mental health service use among Asians is the result of their having fewer mental health needs remains questionable because of a paucity of well-designed studies about mental health service utilization among Asians. Lower mental health service use among Asians has been found to be associated with less perceived need for or awareness of mental health services (5,6,14), limited English proficiency (15–17), and foreign-born status (7,18). Furthermore, people who experienced unfair treatment due to limited English proficiency preferred to use informal services or to seek help from friends or families (17,19).
Study results of mental health service use patterns among subethnic groups have been mixed, but a few studies suggested that Southeast Asians have greater mental health needs and mental health service use compared with other Asian groups (20,21). Comparing patterns of mental health service use among Asians with mental disorders with those of other racial and ethnic groups based on a nationally representative sample is important in elucidating whether efforts to lower the potential health disparity are necessary.
Comprehensive national data about the prevalence of mental health service utilization among Asians have become available through the National Latino and Asian American Study (NLAAS) (3,22). Abe-Kim and others (18) reported that during a 12-month period, 34.1% of Asians with DSM-IV mental disorder diagnoses used any type of mental health services, compared with 41.1% of all individuals in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) sample with DSM-IV mental disorder diagnoses (18). Le Meyer and others (23) also reported that on the basis of the NLAAS, Asians with mental disorders utilized specialty mental health services at a significantly lower rate than did NCS-R participants with mental disorders. Xu and others (11) reported that Asian females underutilized mood and anxiety services compared with non-Hispanic whites.
Even as Abe-Kim and Le Meyer's studies suggest underutilization of mental health services among Asians with mental disorders, generalizabilty of their findings are compromised by the use of an external, general population sample such as the NCS-R as the comparison group. Differences in sampling strategies and adherence to assessment protocols between the two studies may have introduced bias in their findings. Also, these studies did not stratify and compare mental health service use between Asians and other ethnic groups across specific mood, anxiety, and substance use diagnostic groups. Therefore, discrete patterns of mental health service utilization among Asians across specific mental disorder diagnoses have remained unclear.
This study used a nationally representative sample of participants from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC) to examine the rate of mental health service utilization by Asians according to specific diagnoses (24). To address that aim, this study compared the lifetime mental health service utilization among Asians to that of other racial and ethnic groups, including whites, blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, who had been diagnosed as having lifetime mood, anxiety, and substance (alcohol and drug) use disorders.
Methods
Sample
Data are derived from the first wave (2001–2002) of NESARC, sponsored by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The institutional review board of the U.S. Census Bureau and the Office of Management and Budget approved the research protocol, including the informed consent procedure. NESARC is a face-to-face epidemiological survey of noninstitutionalized participants who are aged 18 or older that used a general population-based sampling scheme (24–26). The overall response rate was 81%, and the sample age, race, sex, and ethnicity were weighted and adjusted to reflect the U.S. population as measured by the 2000 decennial census.
A total of 43,093 participants were asked about among other topics, lifetime history of mental disorders, symptoms of mental illnesses in the past 12 months, and mental health service utilization. This study compared the prevalence of psychiatric disorders and diagnosis-specific mental health service utilization patterns among Asians (N=1,332) in the 2001–2002 NESARC cohort with those of whites (N=24,507), blacks (N=8,245), Hispanics (N=8,308), and Native Americans (N=701). Asians were subcategorized based on country of origin as East Asian (N=648), including Chinese (N=306), Japanese (N=175), Korean (N=131), and Taiwanese (N=36); Southeast Asian (N=485), including Filipino (N=223), Indonesian (N=29), Malaysian (N=11), Vietnamese (N=101), Thai, Laotian, Cambodian, or Burmese (N=82), and other Pacific Islander (N=39); or South Asian (N=298), including Indian, Afghan, and Pakistani (N=251) and Iranian (N=47).
Measures
DSM-IV diagnoses.
The DSM-IV diagnoses were based on the NIAAA Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-DSM-IV (AUDADIS-IV) (25), a structured psychiatric interview designed to be administered by trained lay interviewers. The AUDADIS-IV was designed to assess substance use and other psychiatric disorders in large-scale surveys according to DSM-IV criteria (27). Mood disorders diagnosed by AUDADIS-IV consisted of major depressive disorder, dysthymia, and bipolar disorder types I and II. Diagnoses of anxiety disorders included social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, agoraphobia with or without panic disorder, and specific phobia. Mood and anxiety disorders induced by substance use and physical illness were excluded. AUDADIS-IV also assessed alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, drug abuse, and alcohol or drug dependence related to ten different drug classes, including sedatives, tranquilizers, opiates (other than heroin or methadone), stimulants, hallucinogens, cannabis, cocaine (including crack cocaine), inhalants or solvents, heroin, and other drugs.
AUDADIS-IV was not specifically examined in Asian populations, but the test-retest reliability and validity were assessed in the multiracial sample from the 2001–2002 NESARC (9,25). The test-retest reliability of mood and anxiety disorders based on AUDADIS-IV was found to be fair, with kappas of .65 for major depression and .58 for dysthymia and a slightly lower kappa (.42–.48) for anxiety disorders (28). The substance use diagnoses have excellent reliability in clinical and general populations in the United States and abroad, as indicated by a minimum kappa of .74 for alcohol diagnoses and minimum reliability of .79 for drug diagnoses (25,28–30).
Mental health service utilization.
All respondents who met screening criteria for the psychiatric disorder subsections were asked to report on lifetime mental health service utilization for each psychiatric disorder, including major depression, dysthymia, mania, panic attacks, social phobia, specific phobia, and generalized anxiety disorder. Similarly, respondents who met screening criteria for alcohol use disorder and drug use disorder subsections were asked to report on lifetime mental health service utilization for alcohol and drug use disorders. Use of mental health services in the past 12 months was determined by subtracting the respondents' age at the time of latest mental health use from the respondent's current age.
Mental health utilization for those with mood and anxiety disorders included outpatient services (went to physician, counselor, therapist, or other professional for help to improve specific types of mood or anxiety disorders), inpatient services (stayed overnight or longer in a hospital setting), emergency services, or use of prescribed medicine. Alcohol and drug service utilization covered 13 types of services, including Alcoholics Anonymous, Narcotics Anonymous, Cocaine Anonymous, or 12-step meeting; social services for alcohol or drug abuse or dependence; alcohol or drug detoxification ward; inpatient ward of psychiatric or general hospital or community mental health program; emergency services for alcohol or drug use; halfway house or therapeutic community; visit to a crisis center related to substance use; employee assistance program; visit to clergy because of substance use; visits to a private physician, psychiatrist, psychologist, social worker, or other professional; and visits to any other agency or professionals. The study excluded visits to clergy because the nature of spiritual or religious services did not match our definition of outcome-based, formal mental health services.
Ascertainment of race or ethnicity.
Race and ethnicity were identified by asking respondents to answer to the question, “What is your origin or descent?” by choosing from a list of 58 categories.
Statistical analysis
To account for the complex survey design of NESARC, weights and strata were corrected and standard errors were calculated using the subpop and svy linearized commands in the Stata/SE, version 10.0, statistical package. Prevalence and standard errors were calculated using cross-tabulations for each diagnosis of mood, anxiety, and substance use disorder. Mental health service utilization was examined only among respondents who met the criteria of mental health diagnoses investigated by this study. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained using logistic regressions.
As described by Keyes and others (31), variables that we controlled for the regression model were selected from the Andersen model of health services utilization (32,33). Those confounders consisted of predisposing factors (sex and age) and enabling factors (income, education, marital status, and current insurance status). Thus age, sex, family income, education, marital status, and current insurance status were controlled for the analysis of the odds ratio of mental health service utilization across racial and ethnic groups. Further, to address the need for treatment, each model contained a disorder-specific clinical covariate to control for the severity of the disorder. Severity of mood or anxiety disorders was indicated by the total number of mood or anxiety symptoms, respectively. Likewise, severity of substance use or dependence was calculated by the total of alcohol or drug disorder symptoms. The severity indicators were substantially correlated (coefficients=.32–.39) with functional disability, as measured by the 12-item Short-Form Questionnaire (SF-12v) (34).
Results
Demographic variables
Approximately 4.4% of the weighted sample was Asian (N=1,332), 71% was white (N=24,507), 11.1% was black (N=8,245), 11.6% was Hispanic (N=8,308), and 2.1% was Native American (N=701).
Table 1 shows the basic demographic characteristics of Asian, white, black, Hispanic, and Native American participants. Ratios between male and female were similar across racial groups except among blacks, who had a greater proportion of females. Fewer Asian respondents were born in the United States compared with respondents from other racial and ethnic groups. Asians had the highest prevalence of recent immigrants. The highest proportion of respondents with less than a high school education was among Hispanics, followed by Native Americans and blacks. More whites had health insurance than any other group, followed by Native Americans, blacks, Asians, and Hispanics. All differences in demographic characteristics were statistically significant across racial and ethnic groups.
Service utilization for mood or anxiety disorders
The proportion of Asians making use of mental health services for mood or anxiety disorders was the lowest among the racial and ethnic groups (Table 2). Lifetime prevalence of mental health service utilization among Asians with major depression (38.8%) or bipolar disorder (18.8%) was substantially lower than among whites (65.9% and 54.6%, respectively), blacks (46.9% and 39.5%), Hispanics (53.6% and 39.5%), and Native Americans (65.0% and 67.2%). Interestingly, prevalence of mental health service use among Asians with dysthymia (66.3%) was higher than among blacks (59.8%) and Hispanics (63.5%) with the same condition but lower than among whites (80.2%) and Native Americans (78.9%).
The prevalence of mental health service utilization for any anxiety disorder was lower among Asians (24.3%) than among any other racial and ethnic group but was similar to that of blacks (24.7%). Among respondents with specific phobia, Asians (10.5%) underutilized mental health services compared with blacks (14.3%), Hispanics (17.8%), Native Americans (24.7%), and whites (27.4%).
Differences in the prevalence of mood or anxiety disorders between racial and ethnic groups were statistically significant except for social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder.
Service use was higher among South Asians (49.5%) with mood disorders than among East Asians (34.4%) and Southeast Asians (34.7%). Likewise, a higher proportion (34.2%) of South Asians utilized mental health services for anxiety disorders, compared with East Asians (26.8%) or Southeast Asians (34.2%). Regarding the types of mental health service use, Asians had a higher proportion of visits to a counselor, therapist, or doctor compared with whites, Hispanics, and Native Americans but had the lowest use of psychiatric medication of any other racial group (data available upon request).
After adjustment for socioeconomic factors and severity of mood disorder, Asians with a lifetime diagnosis of mood disorders were significantly less likely to use mental health services for the disorder than whites (OR=.31), Hispanics (OR=.49), and Native Americans (OR=.27) but equally likely as blacks (Table 3). Asians with a lifetime diagnosis of anxiety disorders had lower point estimates of the odds of mental health service utilization compared with whites, Hispanics, and Native Americans; however, associations were not statistically significant. Asians and blacks with a lifetime diagnosis of anxiety disorders did not differ significantly in mental health service use. Our separate analysis after adjustment for the variables of U.S.-born status and years lived in the United States did not change results for use of services for mood and anxiety disorders.
Service utilization for substance use disorders
The proportion of lifetime health service utilization among individuals with alcohol and drug disorders did not statistically significantly differ between racial and ethnic groups (Table 2). Likewise, odds of mental health service utilization among Asians with lifetime alcohol and drug abuse or dependence diagnoses did not significantly differ from whites, blacks, or Hispanics (Table 3). A separate analysis showed that adjustment for U.S.-born status and years lived in the United States resulted in marginally significantly higher substance use service utilization among Asians compared with blacks (OR=2.24, CI=1.01–4.96).
Service utilization for any mental disorder
The lifetime prevalence of mental health service utilization among respondents with any lifetime diagnosis of a mental disorder was lowest among Asians (27.8%, Table 2). The odds of mental health service utilization for any lifetime diagnosis of mental disorder were statistically significantly lower among Asians than among whites (OR=.50), Hispanics (OR=.56), and Native Americans (OR=.41) but were no different than among blacks. Adjustment for variables that indicated U.S.-born status and years lived in the United States did not change the inferences (data available upon request).
Discussion
This study reported lower mental health service utilization among Asians with DSM-IV diagnoses of mental disorders than among whites, Hispanics, and Native Americans with the same diagnoses based on a nationally representative sample of adults in the United States. Though data for this study were collected in 2001, there appears to have been little change in the national trend of overall outpatient service use for depression treatment in the past decade (35).
Our findings were consistent with previous reports of underutilization of any mental health services or specialty mental health services among Asians in the United States (18,23). Furthermore, this study specifically found that Asians with lifetime mood disorders, such as major depression and bipolar disorder, significantly underutilized mental health services compared with whites, Hispanics, and Native Americans. This study found no significant difference in mental health service utilization for anxiety disorder and substance abuse disorder among Asians compared with other ethnic groups. It is likely that underutilization by Asians of mental health services specifically for mood disorders accounts for that group's general trend toward underutilization of mental health services for any mental disorder compared with other racial and ethnic groups.
Several previous studies have suggested that U.S.-born Asians have significantly higher prevalence of mental health service utilization than Asian immigrants (18,23,36). Interestingly, however, adjustment for years of residency in the United States or U.S.-born status in our analysis did not appreciably change direction and magnitude of disparity in mental health service utilization across racial and ethnic categories. In other words, race or ethnicity seemed to be a more determinant factor in mental health utilization than nativity or length of residency. Future study should examine in more detail the role of acculturation in mental health service utilization patterns among Asians.
Our study findings underscored the need for psychosocial education and community outreach that especially targets Asians with mood disorders. Previously, stigma attached to mental disorders, somatization of mental health symptoms, unawareness of mental health facilities, and limited English proficiency have been proposed to explain underutilization of mental health services among Asians (17–19,36–42). We speculate that a public campaign targeted to lower the stigma attached to mood disorders and to increase awareness of availability of local mental health services to the Asian community could increase mental health service utilization among Asians with mood disorders. At the same time, providing linguistically appropriate services to Asians with limited English proficiency and educating service providers about culturally specific presentation of mood disorders could improve detection of mood disorders among Asians and their access to treatment.
The analysis had several notable methodological limitations. Assessment of mental health service utilization relied on subjective recall by the study participants. Especially among older respondents, recall bias might have influenced our results. Furthermore, because wave 1 of the NESARC study did not assess posttraumatic stress disorder, which is prevalent among Asian refugee groups affected by war and genocide (20,21), the prevalence of anxiety disorders may have been underestimated. Limited English proficiency, acculturation, or factors associated with lower mental health service use (2,17,18,23,37,40) were not measured by this study. Because visits to nontraditional providers were not measured as part of mood or anxiety disorder treatment and were excluded from the analysis for substance use service use, inferences cannot be made about help seeking from indigenous healers or religious leaders.
Another possible bias in our study findings was a tendency to underreport mental health symptoms and service use, especially among Asians, because of a perception of stigma attached to mental disorders (37–40). Also, despite the robust sample size of the NESARC study, our sample size was insufficient to examine mental service utilization in the past year for respondents diagnosed as having a DSM-IV disorder. Nevertheless among Asian patients past-year utilization was similar in magnitude and directionality with lifetime utilization. [Tables summarizing 12-month prevalence of mental health services utilization and odds ratios of 12-month utilization by racial and ethnic group are available in an online appendix to this report at ps.psychiatryonline.org.]
Similarly, despite the fact that the Asian category consisted of 43 different ethnic groups and more than 100 different languages and dialects (4), the study did not have a large enough sample size to compare mental health service utilization across the Asian subgroups. Asian subethnic groups may have substantial variations in the prevalence of mental illness and service use that may limit the generalizability of our study results to all persons of Asian ancestry. Finally, our analysis was cross-sectional; hence, the study could not examine temporal patterns of mental health service use in relation to the onset or remission of mental disorders. Analysis of predictors of treatment entry based on a prospective study design could yield valuable information about improving access to mental health services among Asians.
Also notable are the strengths of this study. NESARC has a larger sample size and better generalizability for the Asian population compared with previous smaller studies (6,41). Unlike studies that used NLAAS data, this study's use of NESARC data made available diagnostic information on the basis of structured psychiatric assessment. This information gave us an opportunity to stratify and compare mental health service utilization patterns for each specific psychiatric diagnosis across racial and ethnic groups. Furthermore, unlike previous study reports that used an external reference group (18,23), our analysis provided more definitive findings about mental health service differences across several ethnic groups in the same study.
Conclusions
Our findings suggested that even among individuals who have DSM-IV diagnoses of mental disorders, Asians underutilize mental health services compared with members of other racial and ethnic groups. Policy implications of this study include facilitating greater access to psychiatric treatment and increasing culturally sensitive services for Asians, especially those with mood disorders (42). Clinical implications for practitioners include increasing awareness that depression among Asians often goes undetected and increasing empathy for Asians, who experience unique sociocultural stressors (37). Service and research sectors should collaborate in building evidence-based community health care facilities, training existing mental health workers, providing psychoeducation about early detection and treatment of mood disorders, and further identifying barriers to participation in mental health programs by Asians. We speculate that increasing referral bridges to indigenous healers, religious leaders, and care providers would encourage access to mental health services among some members of subethnic Asian groups (43).
1 2008 American Community Survey. Washington, DC, US Census Bureau, American FactFinder. Available at www.factfinder.census.gov. Accessed
2 : Immigration-related factors and mental disorders among Asian Americans. American Journal of Public Health 97:84–90, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
3 : Considering context, place, and culture: the National Latino and Asian American Study. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 13:208–220, 2004 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
4
5 : Racial and ethnic differences in the mental health problems and use of mental health care. Medical Care 43:775–784, 2005 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
6 : Patterns of help-seeking behavior for anxiety disorders among the Chinese speaking Australian community. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 43:872–877, 2008 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
7 : Depressive symptomatology and mental health help-seeking patterns of US and foreign-born mothers. Maternal and Child Health Journal 11:257–267, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
8 : Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV drug abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Archives of General Psychiatry 64:566–576, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
9 : Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independent mood and anxiety disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Archives of General Psychiatry 61:807–816, 2004 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
10 : Epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcoholism and Related Conditions. Archives of General Psychiatry 62:1097–1106, 2005 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
11 : Twelve-month prevalence of psychiatric disorders and treatment-seeking among Asian Americans/Pacific Islanders in the United States: results from the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Journal of Psychiatric Research 45(Epub):910–918, 2011 Crossref, Google Scholar
12 : National utilization of mental health services by Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders. Journal of Community Psychology 25:141–145, 1997 Crossref, Google Scholar
13 : Underutilization of mental health services by Asian Americans residing in the United States. Issues in Mental Health Nursing 19:225–240, 1998 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
14 : Access to specialty mental health services among women in California. Psychiatric Services 56:729–734, 2005 Link, Google Scholar
15 : English language proficiency and mental health service use among Latino and Asian Americans with mental disorders. Medical Care 48:1097–1104, 2010 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
16 : English language proficiency and lifetime mental health service utilization in a national representative sample of Asian Americans in the USA. Journal of Public Health 32:431–439, 2010 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
17 : Access to mental health treatment by English language proficiency and race/ethnicity. Journal of General Internal Medicine 22:289–293, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
18 : Use of mental health-related services among immigrant and US-born Asian Americans: results from the National Latino and Asian American Study. American Journal of Public Health 97:91–98, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
19 : Discrimination and mental health-related service use in a national study of Asian Americans. American Journal of Public Health 12:2410–2417, 2010 Crossref, Google Scholar
20 : Public outpatient mental health services: use and outcome among Asian-Americans. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 64:448–455, 1994 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
21 : Rates and correlates of seeking mental health services among Cambodian refugees. American Journal of Public Health 96:1829–1835, 2006 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
22 : Plan and operation of the National Survey of Health and Stress, the National Survey of American Life, and the National Latino and Asian American Survey. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 13:241–269, 2004 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
23 : Use of specialty mental health services by Asian Americans with psychiatric disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 77:1000–1005, 2009 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
24 : Source and Accuracy Statement: Wave 1 National Epidemiologic Survey of Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC). Bethesda, Md, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 2003 Google Scholar
25 : The Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-IV (AUDADIS-IV): reliability of alcohol consumption, tobacco use, family history of depression and psychiatric diagnostic modules in a general population sample. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 71:7–16, 2003 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
26 : Prevalence, correlates, co-morbidity, and comparative disability of DSM-IV generalized anxiety disorder in the USA: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Psychological Medicine 35:1747–1759, 2005 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
27 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association, 1994 Google Scholar
28 : The Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule (AUDADIS): reliability of alcohol and drug modules in a general population sample. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 39:37–44, 1995 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
29 : Reliability of the alcohol and drug modules of the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule—Alcohol/Drug-Revised (AUDADIS-ADR): an international comparison. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 47:171–185, 1997 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
30 : The Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule-IV (AUDADIS-IV): reliability of new psychiatric diagnostic modules and risk factors in a general population sample. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 92:27–36, 2008 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
31 : Service utilization differences for axis I psychiatric and substance use disorders between white and black adults. Psychiatric Services 59:893–901, 2008 Link, Google Scholar
32 : Measuring access and trends; in Changing the US Health Care System. Edited by Andersen RMRice THKominski GF. San Francisco, Jossey-Bass, 1996 Google Scholar
33 : Revisiting the behavioral model and access to medical care: does it matter? Journal of Health and Social Behavior 36:1–10, 1995 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
34 : Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability of the SF-36 in eleven countries: results from the IQOLA Project. International Quality of Life Assessment. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 51:1149–1158, 1998 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
35 : National trends in the treatment for depression from 1998 to 2007. Archives of General Psychiatry 61:1265–1273, 2010 Crossref, Google Scholar
36 : Psychiatric disorders among foreign-born and US-born Asian-Americans in a US national survey. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 41:943–950, 2006 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
37 : Changes in the sociocultural reality of Chinese immigrants: challenges and opportunities in help-seeking behavior. International Journal of Social Psychiatry 56:436–447, 2010 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
38 : Attitudes toward mental health services: age-group differences in Korean American adults. Aging and Mental Health 13:127–134, 2009 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
39 : Racial and ethnic disparities in mental illness stigma. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 195:1020–1023, 2007 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
40 : Identifying individual and contextual barriers to seeking mental health services among Korean American immigrant women. Issues in Mental Health Nursing 30:78–85, 2009 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
41 : Effects of psychoeducation for Korean Americans with chronic mental illness. Psychiatric Services 53:1125–1131, 2002 Link, Google Scholar
42 : Culturally sensitive collaborative treatment for depressed Chinese Americans in primary care. American Journal of Public Health 100:2397–2402, 2010 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
43 : Engaging Asian Americans for mental health research: challenges and solutions. Journal of Immigrant Health 7:109–116, 2005 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
Figures and Tables
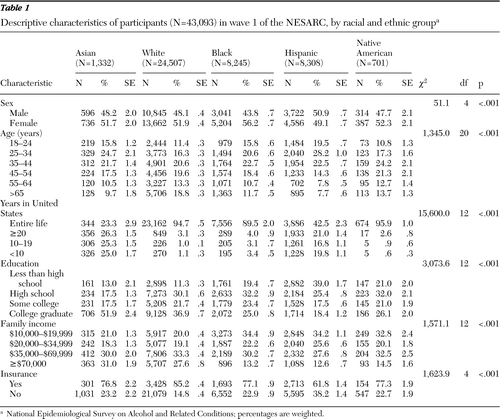
Table 1 Descriptive characteristics of participants (N=43,093) in wave 1 of the NESARC, by racial and ethnic group
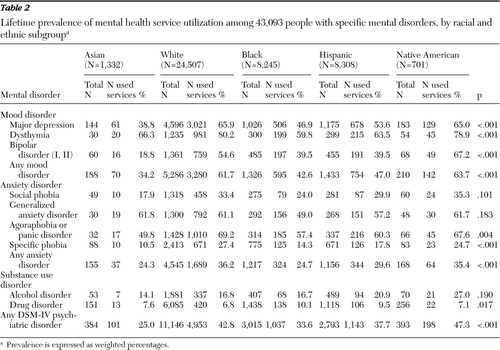
Table 2 Lifetime prevalence of mental health service utilization among 43,093 people with specific mental disorders, by racial and ethnic subgroup
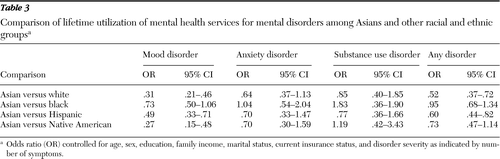
Table 3 Comparison of lifetime utilization of mental health services for mental disorders among Asians and other racial and ethnic groups



